Electric current is a fundamental topic in electricity and electronics. One of the most frequently asked questions is whether the current in the houses is alternating or direct. In this article, we will jump to the topic of the detector and provide unique and valuable content on this topic.
Is the Current in Houses Alternating or Continuous?
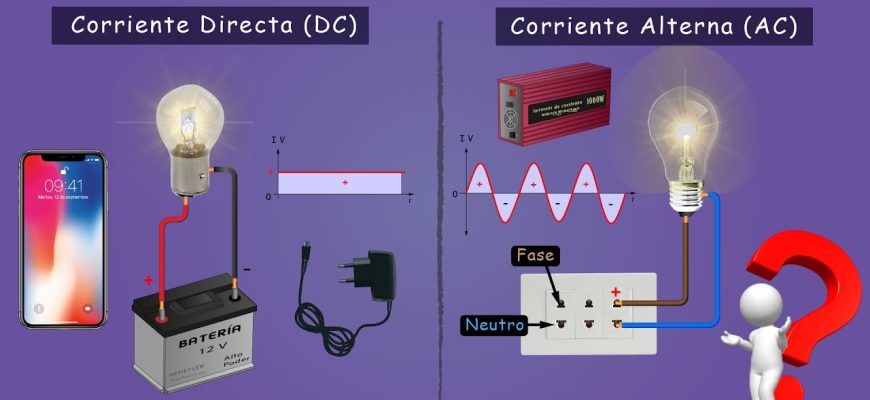
Alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical current in which the flow of electrons changes direction at regular intervals or in cycles. It is the current used in power lines and the electricity normally found in home outlets. In the United States, the standard current is 60 cycles per second (60 Hz), while in Europe and most of the world it is 50 cycles per second (50 Hz).
On the other hand, direct current (DC) is an electrical current that flows constantly in one direction, such as that found in a flashlight or battery-powered devices.
One of the advantages of alternating current is its ability to change voltage more economically. Furthermore, the energy loss when transporting the current over long distances is less compared to direct current.
What is the normal current of a house?
In regions where 230 V or 127 V voltages are used, it is common to use a three-phase system for electrical distribution in homes and businesses. In Europe, the nominal voltage between phase and neutral is 230 V, which implies that the voltage between phases under ideal conditions is 230 V × √3 ≈ 398 V.
In countries like Mexico and others in Latin America, a three-phase system with a voltage of 220 V between phases is used for domestic and commercial electrification; The voltage between phase and neutral is 220 V/√3 ≈ 127 V. In both systems mentioned, the plugs are connected between phase and neutral. Some large loads, such as air conditioning equipment, are connected between two phases (without using the neutral) at 220 V or 230 V (as appropriate). Three-phase motors can be connected using all three phases without the need for the neutral.
In the United States, the electrical system is more complex and presents difficulties, without this resulting in a benefit. Different systems are used for residential and commercial use. For domestic use, a single-phase split-phase system is used, with a nominal voltage of 240 V between phases and 120 V between any phase and neutral. Larger loads, such as air conditioners, are connected between phases.
It is not possible to directly connect three-phase motors or change the transformer for a three-phase one. For businesses and light industries, a three-phase system is used with a voltage of 120 V between any phase and neutral, and 120 V × √3 ≈ 208 V between phases.
Loads designed for 240 V in residential environments cannot be used in commercial applications with this system unless they are designed to also accept 208 V or an additional transformer is used, which involves costs and energy losses. The systems used in Mexico and Europe do not have this disadvantage.
In addition, in the United States there is also an asymmetric three-phase electrical system that is fed by three single-phase transformers in a triangle configuration grounded in the central winding of one of them; the voltage between phases is 240 V. The voltage between phase and neutral is 120 V for two phases and 208 V for the third; Only a small load can be connected between any phase and neutral.
How do you know if the current is alternating or direct?
The main difference lies in the movement of electrons within an electrical conductor.
In the case of alternating current, the electrons move in an oscillatory manner, constantly changing direction, from the negative pole to the positive pole and vice versa. On the other hand, in direct current, electrons move in only one direction, from the negative pole to the positive pole.
Characteristics of alternating current and direct current:
– Amount of energy transported: Alternating current is suitable for transporting energy over long distances from distant cities and offers greater power. On the other hand, direct current is not efficient for long distances, since it loses power during transmission.
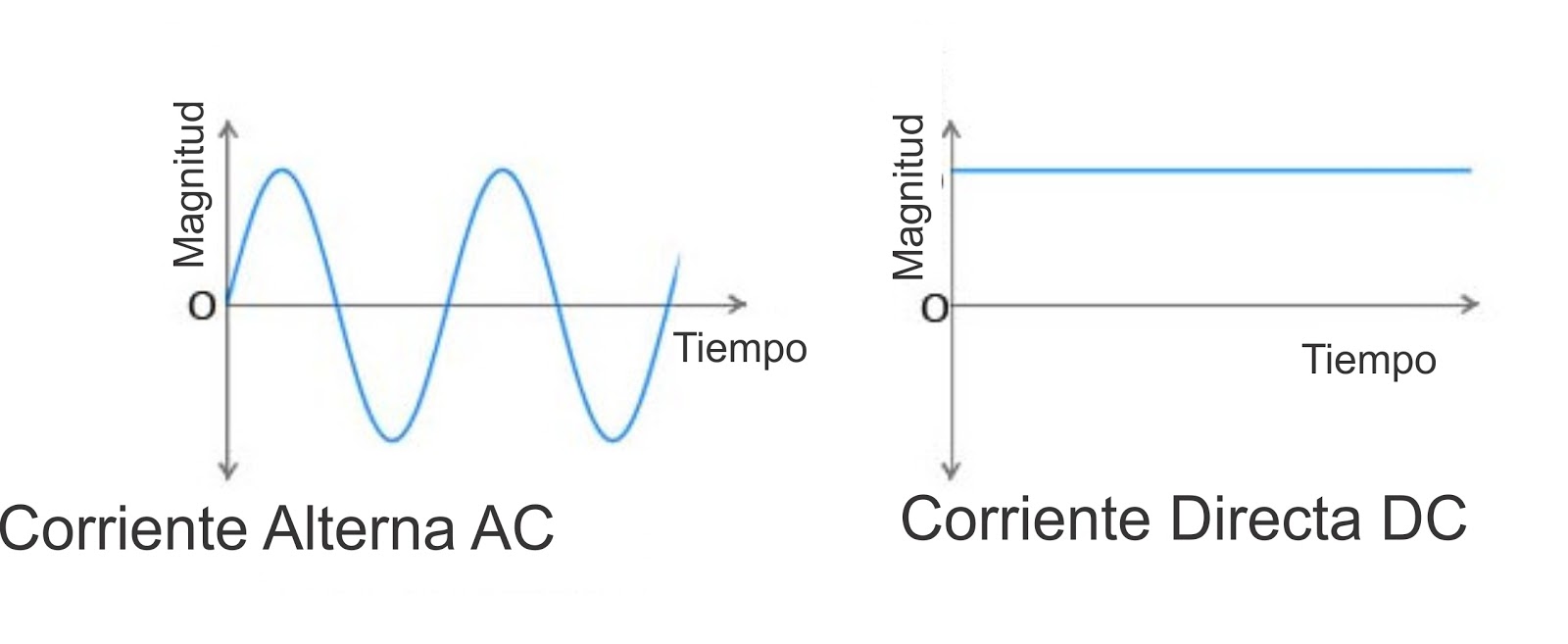
– Frequency: Alternating current has a frequency of 50Hz or 60Hz, depending on the country, which indicates the number of complete cycles per second. In contrast, direct current does not have a specific frequency, since its flow is constant.
– Direction of flow: Alternating current reverses its direction as it flows through a circuit, while direct current flows in a single direction in the circuit.
– Current magnitude: In alternating current, the magnitude of the current varies with time, while in direct current, the current has a constant magnitude.
– Electron flow: In alternating current, electrons constantly change direction during their flow. In direct current, electrons keep their flow in a forward direction.
– Source of obtaining: Alternating current is obtained from an alternating current generator and the electrical grid, while direct current is obtained from cells or batteries.
– Passive parameters: In alternating current, impedance is considered, which includes resistance and reactance. In direct current, only the resistance in the circuit is considered.
How do I know what type of current I have in my house?
After contacting the authorized dealer, you can check the voltage in your house by checking the electrical network. To do so, you can go to the back of the electric meters located in your home. There you should find voltage information, which will tell you the voltage of the supply line.
It is important to keep in mind that electric current can be of two types: alternating or direct, and both have their particular applications and benefits. Instead of focusing on who discovered each type, it is more relevant to understand how they work and how to take advantage of them in various situations.